Introduction
SSO Extension configuration allows seamless single sign-on for iOS and macOS devices by enabling secure, passwordless authentication with identity providers. It streamlines the login experience across apps and websites using native OS support.
Creating the configuration
Provide a name to this configuration.
Remove this configuration when relaxing the policies on the device: When this option is enabled, the configuration will be automatically removed in the following scenarios: when policies are relaxed, or the device is unlocked via the dashboard, and when the device is deleted, all associated configurations and data will be cleared from the device.
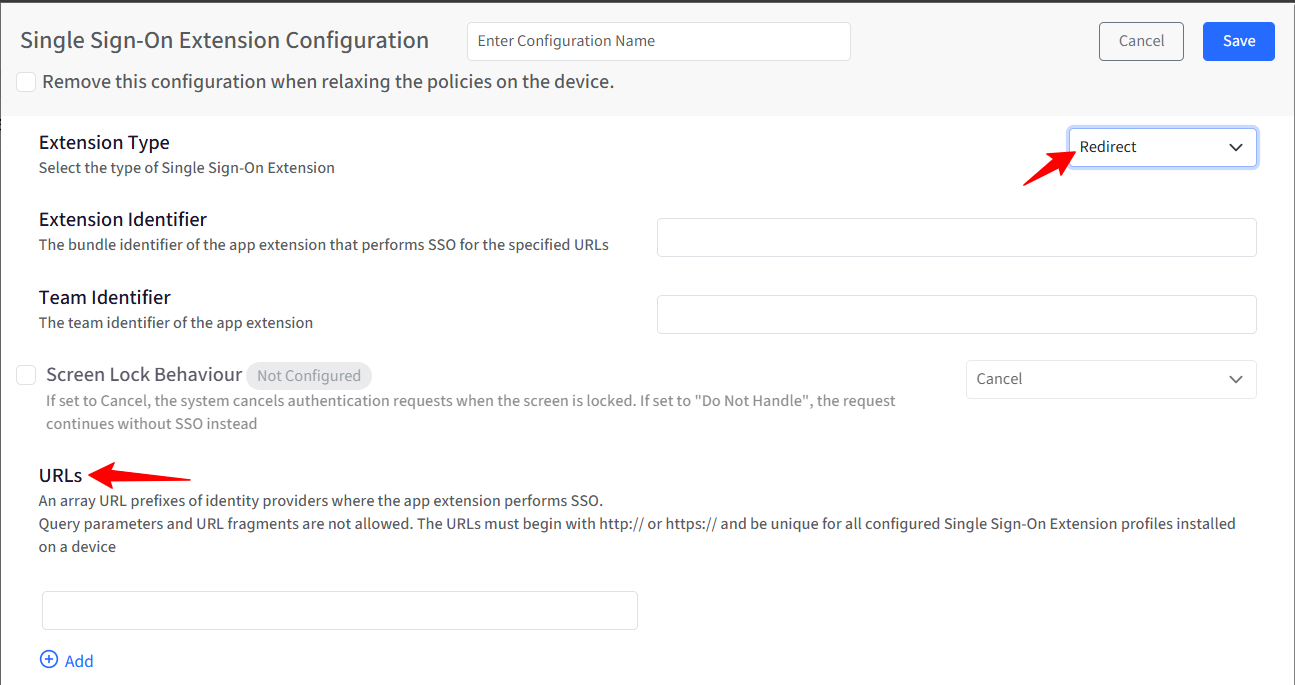
Extension Type: Defines how the SSO extension performs authentication.
Credential (Default): Uses credentials (such as Kerberos or identity-provider-issued credentials) to authenticate apps silently.
Redirect: Redirects authentication requests to a web-based identity provider (for example, SAML or OIDC flows).
Extension Identifier: Specifies the bundle identifier of the app extension that performs SSO. This value must exactly match the extension’s bundle ID provided by the identity solution vendor and is required for the SSO extension to function correctly. For example, com.example.sso.extension
Team Identifier: Identifies the Apple Developer Team that signed the SSO extension. Helps macOS and iOS verify that the extension is from a trusted developer. It is optional, but recommended for additional validation and security.
Note:
Based on your selection in Extension type in point 2, the available settings on this screen change based on the selected extension type.
Realm: If you have selected Credential in the Extension type, you will have to provide a realm name for the credential payload. It defines the authentication realm used for credential-based SSO and is commonly used with Kerberos-based authentication. As realms are case-sensitive, you must use correct capitalization. For example, EXAMPLE.COM
Hosts: Specifies the domains or hosts for which the SSO extension should handle authentication. Apps connecting to these hosts will automatically use the configured SSO extension. You can add multiple host or domain entries. The maximum supported entries are 25. For example, login.example.com, .example.com
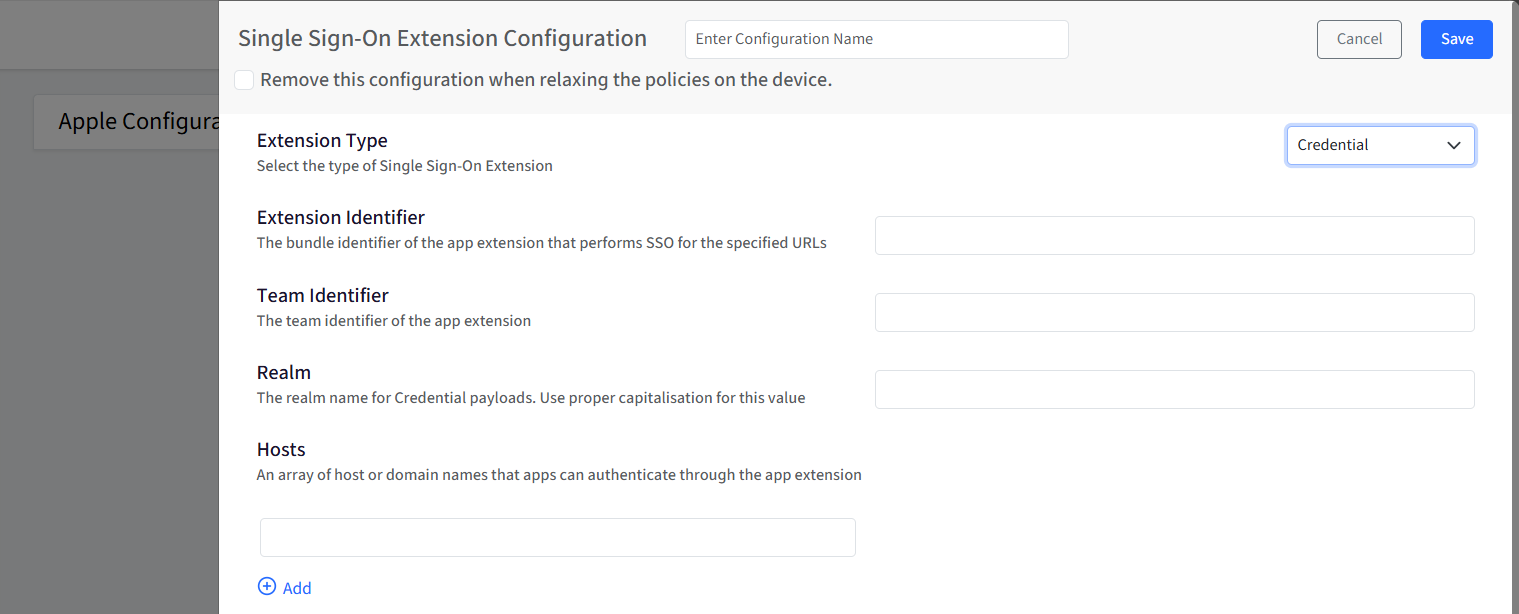
Screen Lock Behaviour: Controls how authentication requests are handled when the device screen is locked. By default, this setting is Not Configured. Select the checkbox to change the state to Configured.
Cancel: Authentication requests are cancelled if the screen is locked.
Do Not Handle: The request continues without SSO and falls back to the app’s default authentication flow.

URLs: If you have selected Redirect in the Extension type, you will have to provide an array of URL prefixes of identity providers where the app extension performs SSO. Please note that Query parameters and URL fragments are not allowed. The URLs must begin with http:// or https:// and be unique for all configured Single Sign-On Extension profiles installed on a device. It supports up to 25 entries.
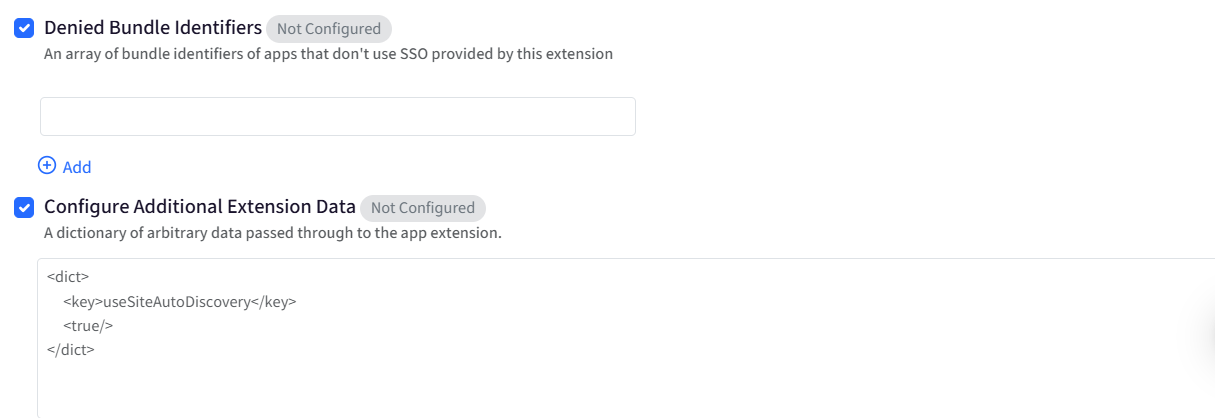
Denied Bundle Identifiers: Excludes specific apps from using this SSO configuration. Apps listed here will not use the configured SSO extension. It is useful when certain apps must authenticate independently. It supports up to 25 entries. Please note that it is supported from iOS 15 and macOS 12 and above. By default, this setting is Not Configured. Select the checkbox to change the state to Configured.
Configure Additional Extension Data: Allows passing custom configuration data directly to the SSO extension. This section is optional and should be configured only if required by your identity provider. Accepts a dictionary (XML plist format) with key-value pairs. Used for advanced or vendor-specific settings not exposed in the UI. By default, this setting is Not Configured. Select the checkbox to change the state to Configured.
This configuration forms the foundation for enabling seamless, secure authentication across managed apps and services using Apple’s Single Sign-On framework.