Windows Delivery Optimization (DO) is a feature used to streamline the distribution of software updates and applications to managed devices. By enabling devices to download content from other nearby devices on the network, instead of relying exclusively on servers, DO helps minimize network bandwidth usage and improves download speeds across the organization.
Key Benefits:
Peer-to-Peer Sharing: Allows devices within the same local network to share updates and app installations with each other. This reduces the need to repeatedly download the same files from Microsoft servers, speeding up the process and saving internet bandwidth.
Bandwidth Management: Administrators can configure bandwidth limits for both upload and download operations, optimizing network usage through Delivery Optimization.
Reduced Download Times: With peer-to-peer sharing, updates are delivered faster, especially in environments with limited internet bandwidth.
Centralized Configuration: IT administrators can set policies for Delivery Optimization, and how much bandwidth can be allocated for peer-to-peer sharing.
Pre-requisites:
a. Enabled Scalefusion MDM agent-based Update Management in Global Windows OS Updates Configuration.
OR
b. Any of Scalefusion Agent-Based Settings or Windows MDM-based settings should be enabled.
Configure Delivery Optimization
Start by creating a Windows Device Profile or Edit an existing one. Navigate to Device Profiles & Policies > Device Profiles and edit an existing profile or create a new Windows profile.
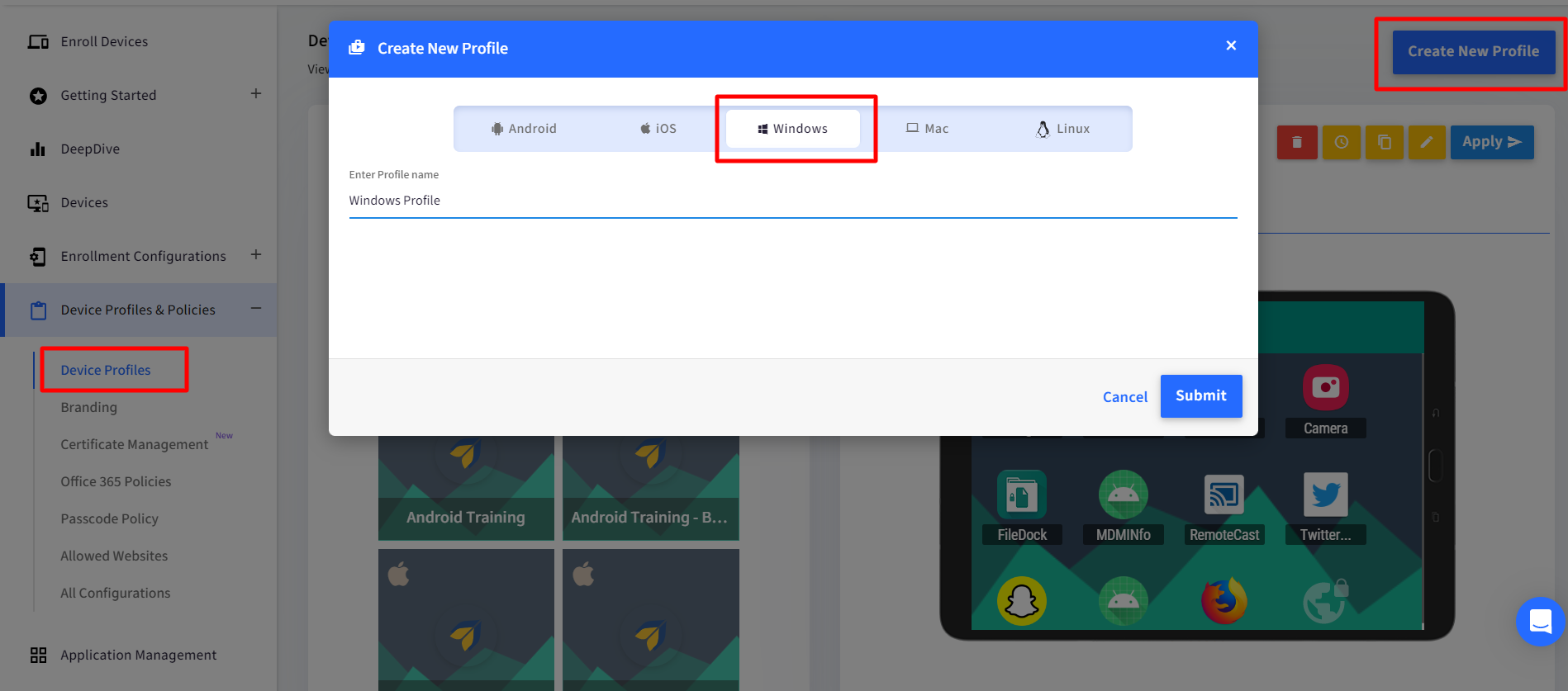
In the Device Profile, navigate to Settings > Windows Updates > Delivery Optimization Settings.
You can Configure Delivery Optimization Via:
Windows CSP
Scalefusion MDM Agent
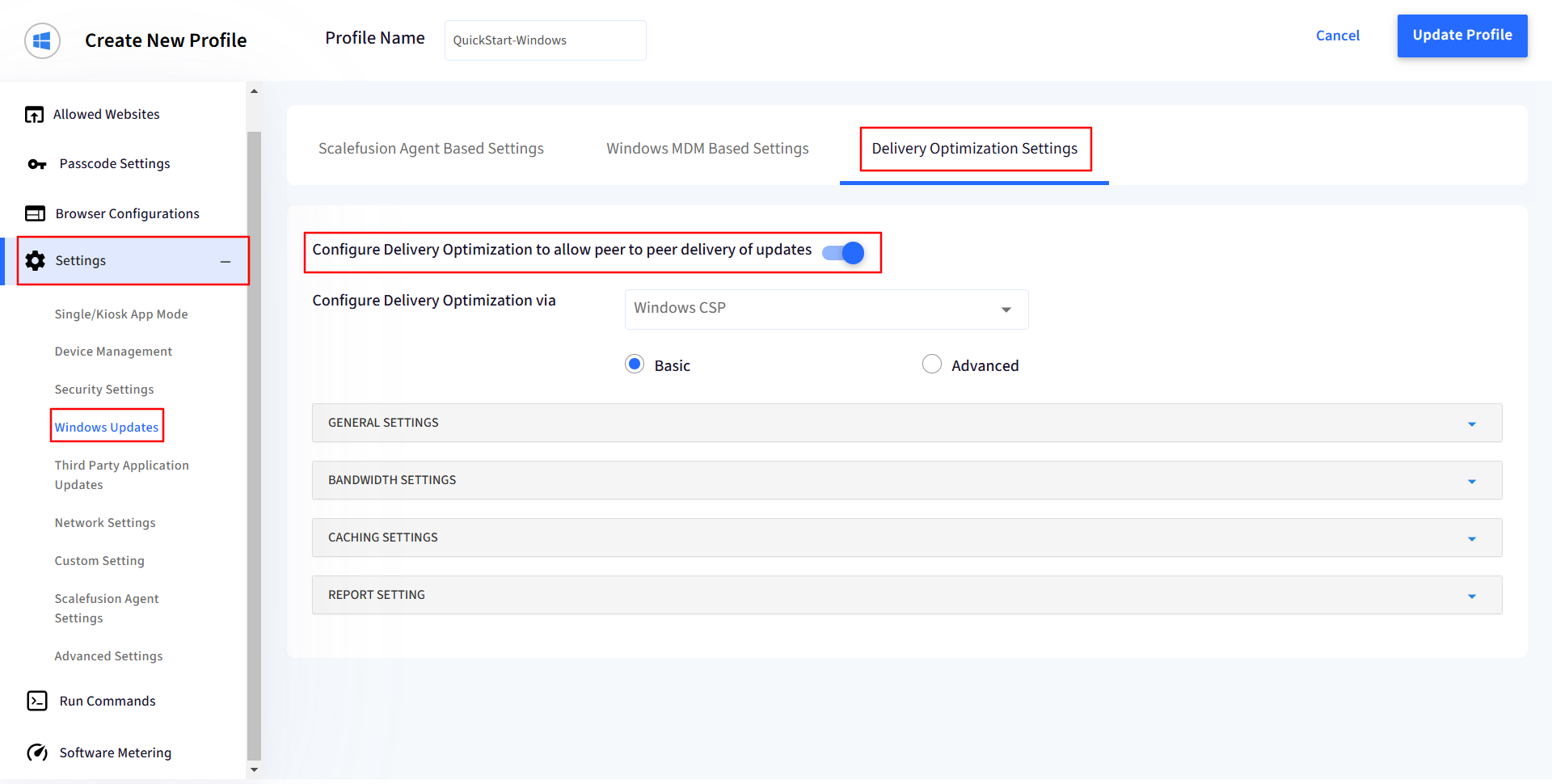
Basic
General Settings:
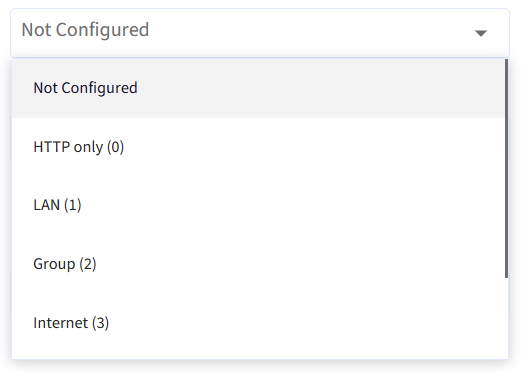
Download Mode - Specifies the download method for downloads of Windows Updates, Apps and App updates
a. LAN (1): LAN allows devices to share portions of downloaded updates and applications with other nearby devices on the same network.
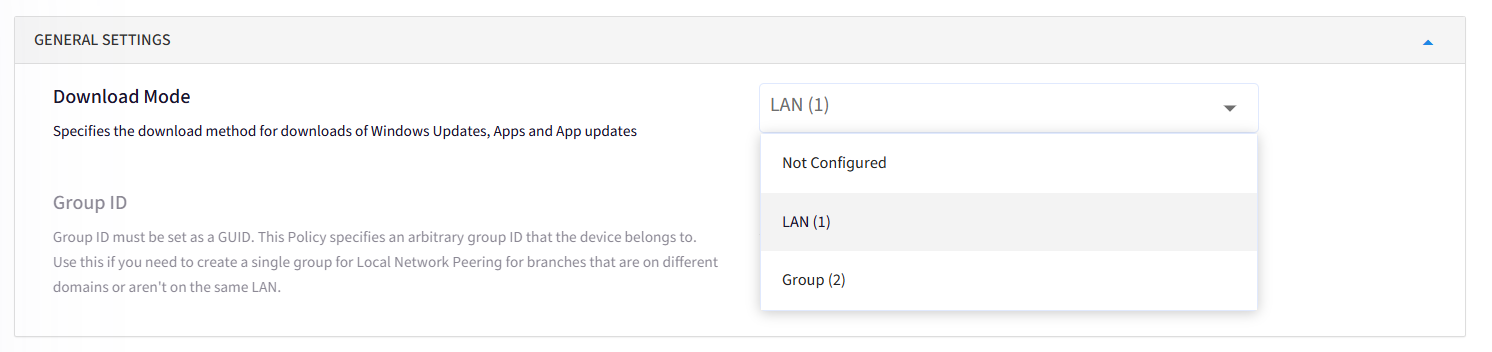
b. Group (2): If Selected, Group ID must be set as a GUID. This Policy specifies an arbitrary group ID to which the device belongs. Use this if you need to create a single group for Local Network Peering for branches that are on different domains or aren't on the same LAN. Click on Generate GUID or Enter your GUID:
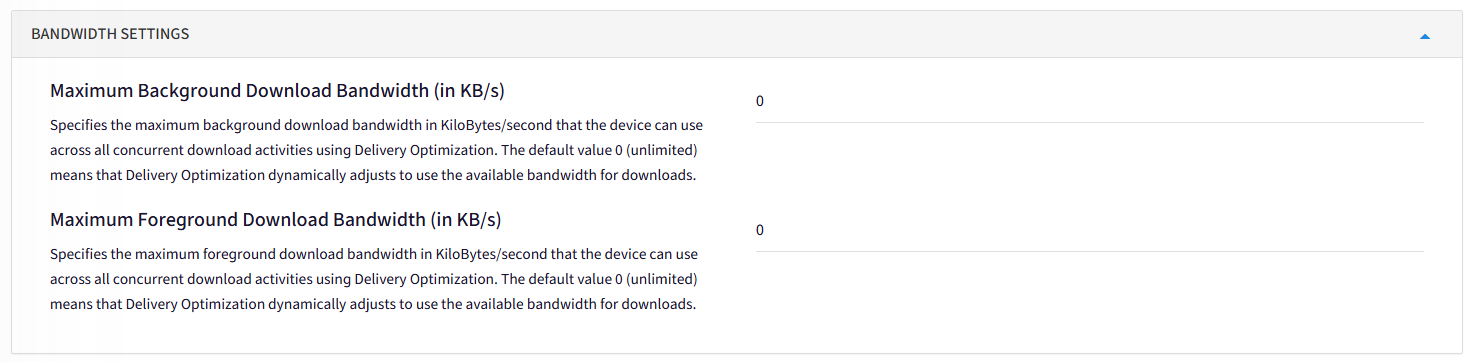
Bandwidth Settings: Specifies the maximum Background & Foreground download bandwidth in KiloBytes/second that the device can use across all concurrent download activities using Delivery Optimization. The default value 0 (unlimited) means that Delivery Optimization dynamically adjusts to use the available bandwidth for downloads.
a. Maximum Background Download Bandwidth (in KB/s)
b. Maximum Foreground Download Bandwidth (in KB/s)
Caching Settings:
Settings | Description |
|---|---|
Minimum RAM required for peer caching (in GB) | Specifies the minimum RAM size in GB required to use Peer Caching. For example, if the minimum set is 1 GB, then devices with 1 GB or higher available RAM will be allowed to use Peer caching. The recommended value is 4 GB (1-100000). |
Minimum disk size required for peer caching (in GB) | Specifies the required minimum disk size (capacity in GB) for the device to use Peer Caching. The recommended value is 32 GB (1-100000). |
Minimum content file size for peer caching (in MB) | Specifies the minimum content file size in MB enabled to use Peer Caching. The recommended value is 10 MB (1-100000). |
Minimum battery level required to upload (in %) | Minimum battery level required to upload data to peers while on battery power. Uploads will automatically pause when the battery level drops below the set minimum battery level. The recommended value is 40%. (0-100). |
Maximum cache age (in seconds) | The maximum retention period for each content item in the cache. The recommended value is 7 days. (0-3650 days). |
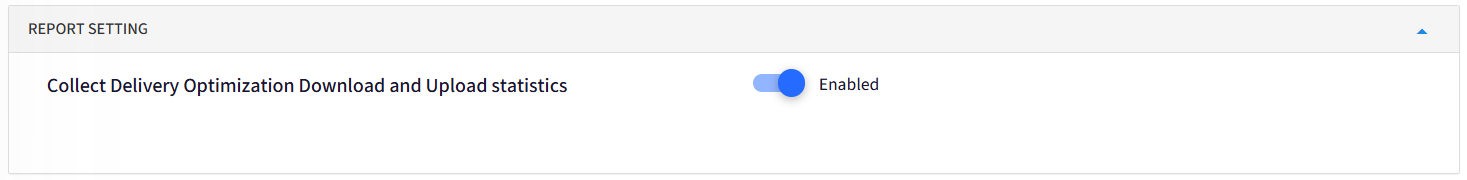
Report Setting: You can Enable/Disable Collect Delivery Optimization Download and Upload statistics from this setting.
Advanced
General Settings:
Download Mode - Specifies the download method for downloads of Windows Updates, Apps and App updates
Download Mode | Configuration | |
|---|---|---|
HTTP (0) | NA | NA |
LAN (1) |
|
|
Group (2) |
|
|
Internet (3) | NA | NA |
Simple (99) | NA | NA |
Bypass Mode(Use BITS instead of Bypass Mode) | NA | NA |
Bandwidth Settings:
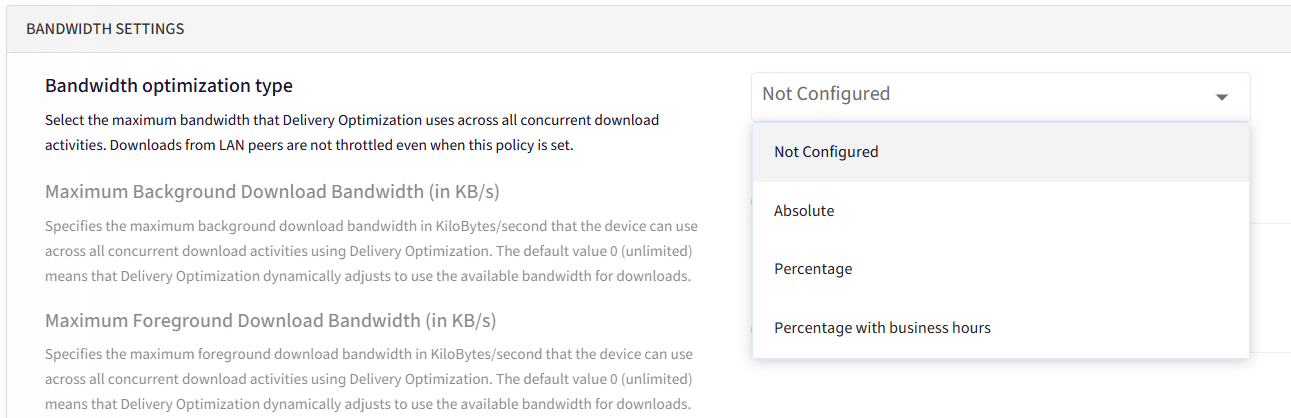
Bandwidth Optimization Types | Configuration |
|---|---|
Absolute |
|
Percentage |
|
Percentage with Business hours |
|
Default Options |
|
Caching Settings: Caching settings are used in Windows Delivery Optimization to store parts of updates or application files locally on a device, allowing it to share those cached pieces with other devices on the network, thus reducing overall bandwidth usage by downloading content from nearby peers instead of always going directly to the internet source.
Caching Configuration | Explaination |
|---|---|
Minimum RAM required for peer caching (in GB) | Specifies the minimum RAM size in GB required to use Peer Caching. For example if the minimum set is 1 GB, then devices with 1 GB or higher available RAM will be allowed to use Peer caching. The recommended value is 4 GB (1-100000). |
Minimum disk size required for peer caching (in GB) | Specifies the minimum RAM size in GB required to use Peer Caching. For example if the minimum set is 1 GB, then devices with 1 GB or higher available RAM will be allowed to use Peer caching. The recommended value is 4 GB (1-100000). |
Minimum content file size for peer caching (in MB) | Specifies the minimum content file size in MB enabled to use Peer Caching. The recommended value is 10 MB (1-100000). |
Minimum battery level required to upload (in %) | Minimum battery level required to upload data to peers while on battery power. Uploads will automatically pause when the battery level drops below the set minimum battery level. The recommended value is 40%. (0-100). |
Modify cache drive | The device drive that Delivery Optimization will use for its cache. The drive location can be specified using environment variables, drive letter or full path. |
Maximum cache age (in seconds) | The maximum retention period for each content item in the cache. The recommended value is 7 days. (0-3650 days). |
Maximum cache size type
| The maximum retention period for each content item in the cache. The recommended value is 7 days. (0-3650 days). |
VPN peer caching
| Enables the device to participate in peer caching while connected via VPN to the domain network. |
Local Server Setting: The option to utilize other devices on your local network as a source for downloading updates and applications, essentially allowing computers to share portions of downloaded content with each other instead of relying solely on Microsoft servers.
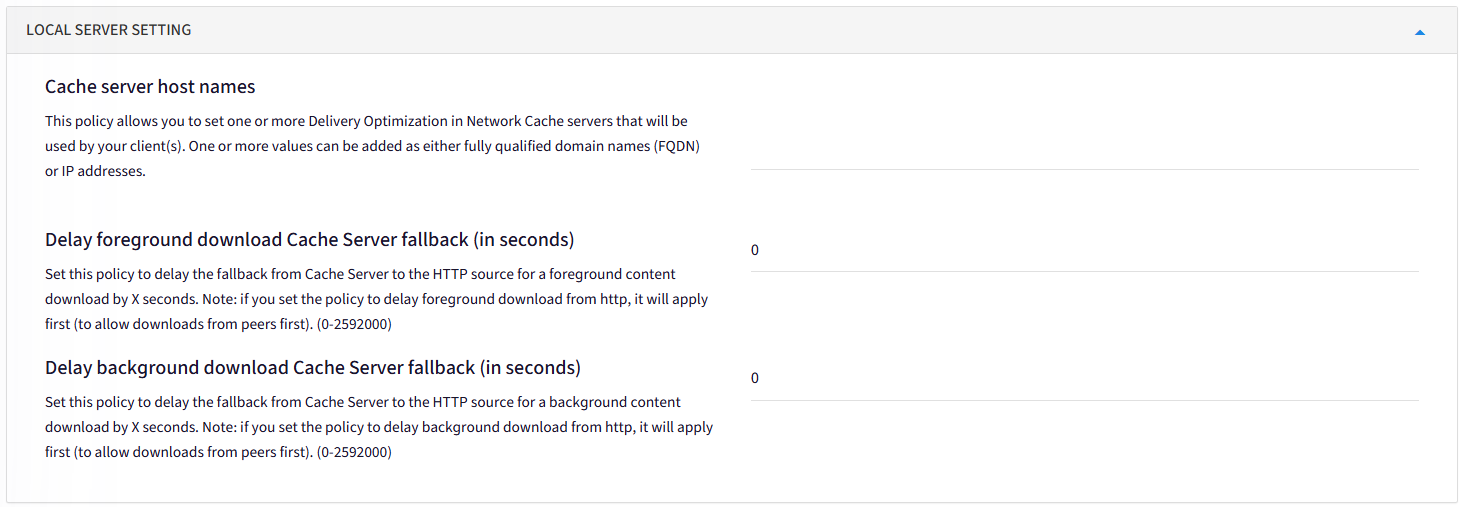
a. Cache server host names - This policy allows you to set one or more Delivery Optimization in Network Cache servers that will be used by your client(s). One or more values can be added as either fully qualified domain names (FQDN) or IP addresses.
b. Delay foreground download Cache Server fallback (in seconds) - Set this policy to delay the fallback from Cache Server to the HTTP source for a foreground content download by X seconds. Note: if you set the policy to delay foreground download from http, it will apply first (to allow downloads from peers first). (0-2592000)
c. Delay background download Cache Server fallback (in seconds) - Set this policy to delay the fallback from Cache Server to the HTTP source for a background content download by X seconds. Note: if you set the policy to delay background download from http, it will apply first (to allow downloads from peers first). (0-2592000)
Report Setting: You can Enable/Disable Collect Delivery Optimization Download and Upload statistics from this setting.

Once you have configured the OS Update policy, save the Device Profile and apply it to the device where you want these changes to take effect.
Allowed URLs for Windows Updates Delivery Optimization:
If you are using Scalefusion to manage Windows OS Updates Delivery Optimization, then please allow the below URLs:
URL/Domain/FQDN | Description |
*.prod.do.dsp.mp.microsoft.com | For communication between clients and the Delivery Optimization cloud service |
*.dl.delivery.mp.microsoft.com *.windowsupdate.com | For Delivery Optimization metadata |
win1910.ipv6.microsoft.com | For group peers across multiple NATs (Teredo) |
https://*.prod.do.dsp.mp.microsoft.com | Delivery Optimization service endpoint |
http://*.windowsupdate.com https://*.delivery.mp.microsoft.com https://*.update.microsoft.com https://tsfe.trafficshaping.dsp.mp.microsoft.com |
|
Delivery Optimization uses specific ports for update delivery: port 7680 (TCP) for peer-to-peer communication within a local network, port 3544 (UDP) for cross-NAT connections via Teredo when using "Group" or "Internet" download modes, and port 443 (HTTPS) for communication with the cloud service. If port 7680 is blocked, peer-to-peer functionality is disabled, but updates can still be downloaded via HTTP/HTTPS.
Courtesy: Microsoft