Use this script to start the System services on Linux machines.
Copy and save the contents below to a UTF-8 editor like notepad++ OR Sublime Text in Windows or gedit in Ubuntu.
If you are using notepad++ then use the bottom right panel to change the type to Unix (LF).
Or click here to download the file.
#!/bin/bash # Define the service names to start service_names=("Service1" "Service2") # Function to check if a service is already running check_service_status() { local service_name="$1" if systemctl is-active --quiet "$service_name"; then echo "Service $service_name is already running." return 0 # Service is already running else return 1 # Service is not running fi } # Start each service for service_name in "${service_names[@]}"; do # Check if the service is already running if check_service_status "$service_name"; then continue # Skip starting the service if it's already running fi # Start the service sudo systemctl start "$service_name" # Check if the service started successfully if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then echo "Service $service_name started successfully." else echo "Failed to start service $service_name." fi doneIn the script, replace the following placeholder:
Provide the service(s) name in the script.
# Define the service names to startservice_names=("Service1" "Service2")
For example,
service_names=("ssh" "NetworkManager" "systemd-journald")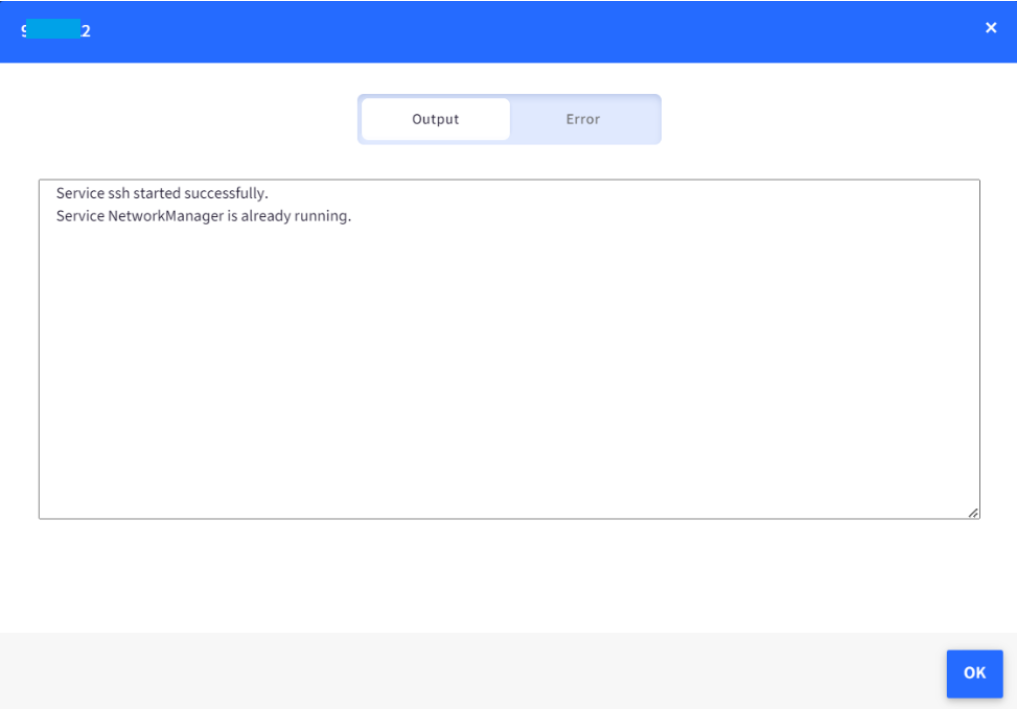
Follow our guide to upload & publish the script using Scalefusion Dashboard.
Note:
Some of the scripts and their contents are sourced from internet and yes, our new friend ChatGPT.
Please validate the scripts on a test machine before deploying them on all your managed devices.
Scalefusion has tested these scripts, however Scalefusion will not be responsible for any loss of data or system malfunction that may arise due to the usage of these scripts.