The following PowerShell script will help the IT Admins to format the OS and non-OS Drives on Windows 10 & above devices.
- Create a file on your desktop, for example, format_nonOS_OS_drive.ps1 and open it in a text editor like notepad++
- Copy the contents below to the file or click here to download the file.Shell
#Format Non OS Drives $winvolume = Get-Volume $osdrive = (Get-CimInstance -ClassName CIM_OperatingSystem).SystemDrive $trimosdrive = $osdrive.SubString(0,1) foreach($vol in $winvolume) { # Don't format OS Drive, CD-ROM Drive and Removable (like Floppy Drive) Drives if ($vol.filesystem -ne $null -and $vol.driveletter -ne $null -and $vol.DriveType -eq "Fixed" -and $vol.driveletter -ne $trimosdrive) { #Write-Host $vol.driveletter Format-Volume -driveletter $vol.driveletter -Full -Force } } #Delete Data folders (exclude system/os folders) from OS Drive $OSDrivePath = $osdrive + "\" $FolderFileItems = Get-Childitem -Path $OSDrivePath $WindowsFolder = Get-Childitem -Path Env:windir $ProgramFilesFolder = Get-Childitem -Path Env:ProgramFiles $ProgramFilesx86Folder = Get-Childitem -Path "Env:ProgramFiles(x86)" $ProgramDataFolder = Get-Childitem -Path Env:ProgramData $UsersFolder = "C:\Users" foreach ($Item in $FolderFileItems) { $ItemName = $Item.FullName if($ItemName -ne $WindowsFolder.Value -and $ItemName -ne $ProgramFilesFolder.Value -and $ItemName -ne $ProgramFilesx86Folder.Value -and $ItemName -ne $ProgramDataFolder.Value -and $ItemName -ne $UsersFolder) { #Write-Output $ItemName Remove-Item $ItemName -Force -Recurse -Confirm:$False -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue } } - This is a PowerShell script that performs the following actions:
- Get the list of volumes using the 'Get-Volume' command and store it in the '$winvolume' variable.
- Get the system drive (OS drive) using the 'Get-CimInstance' command and store it in the '$osdrive' variable.
- Trim the drive letter from the system drive path and store it in the '$trimosdrive' variable.
- Loop through each volume in the '$winvolume' list and format the fixed drives excluding the system drive and CD-ROM and removable drives using the 'Format-Volume' command.
- Get the path of the OS drive and store it in the '$OSDrivePath' variable.
- Get the list of items in the OS drive using the 'Get-Childitem' command and store it in the '$FolderFileItems' variable.
- Get the paths of important system folders (Windows, Program Files, Program Files (x86), Program Data) and store them in separate variables.
- Loop through each item in the '$FolderFileItems' list and delete all the data folders (excluding the important system folders) using the 'Remove-Item' command.
- Once the script is successfully executed, you will be able to see the status of the same in the View Status report on the Scalefusion dashboard.
- Click on the PowerShell script and click on the View Status report.
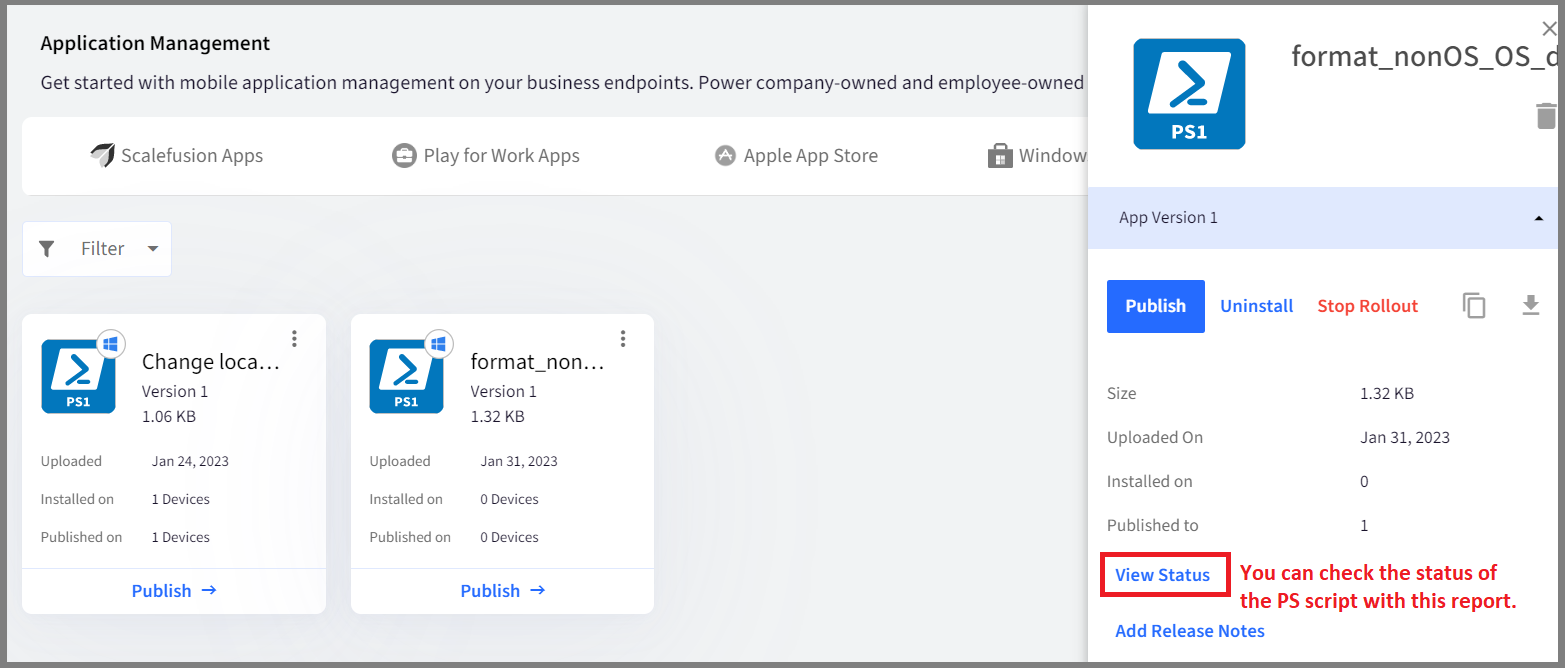
- Executed means that the script has run successfully on the device.
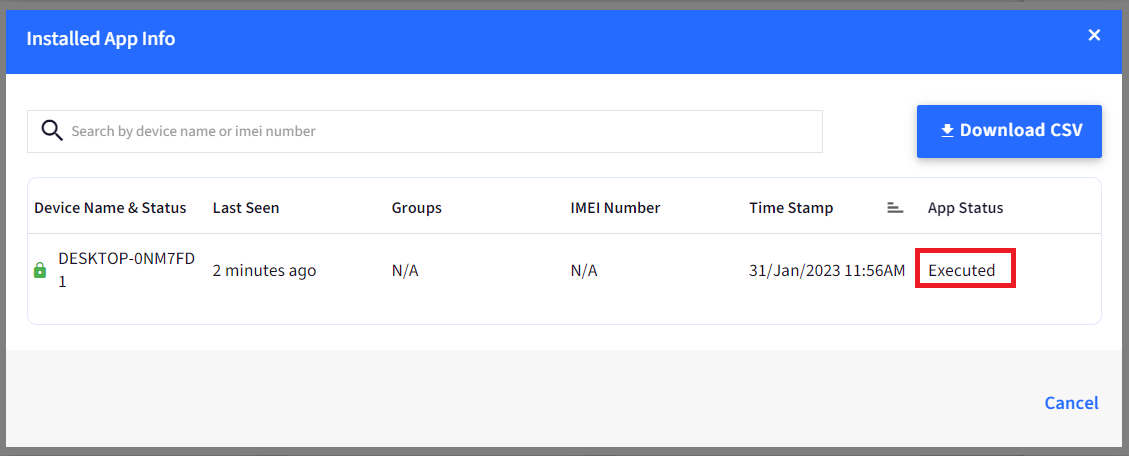
- Click on the PowerShell script and click on the View Status report.
Please note that to use the PowerShell scripts, the Scalefusion MDM Agent Application must be installed on the device(s). Please follow our guide to publish and install the Scalefusion MDM Agent Application.
Notes:
- The scripts and their contents are sourced from various albeit authenticated Microsoft sources and forums.
- Please validate the scripts on a test machine before deploying them on all your managed devices.
- Scalefusion has tested these scripts, however, Scalefusion will not be responsible for any loss of data or system malfunction that may arise due to the incorrect usage of these scripts.