BitLocker is Microsoft’s built-in full-volume encryption feature designed to protect data by providing encryption for the hard disk volumes. It integrates with the operating system and addresses the threats of data theft or exposure from lost, stolen, or inappropriately decommissioned computers.
BitLocker works best on computers with Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 1.2 or later. TPM is a hardware component installed in many newer computers by computer manufacturers. It works with BitLocker to help protect user data and to ensure that a computer has not been tampered with while the system is offline.
On computers that do not have TPM version 1.2 or later, you can still use BitLocker to encrypt the Windows operating system drive. However, this implementation will require the user to insert a USB startup key to start the computer or return from hibernation.
Scalefusion lets IT Admins configure BitLocker settings and apply these settings to managed Windows 10 and above devices. Further on Azure AD joined devices the BitLocker encryption can be enforced and automated.
Prerequisites
BitLocker requires Windows 10 v1809+ and above to work on Windows Pro, Enterprise, and Education Editions.
Not Supported on Windows Home (10 & 11).
The following document guides you on how to set up BitLocker and push the configuration on devices. We also cover the user experience once the BitLocker policy is pushed to devices.
If not configured correctly, the settings provided by BitLocker could lead to conflicts. Please review our Conflicting Scenarios section to familiarize yourself with the settings.
Setting up BitLocker in Windows Profile
The first step is configuring a BitLocker policy that can be pushed to devices. Follow the steps below to configure a BitLocker policy:
Sign In to your Scalefusion Dashboard.
Navigate to Device Profiles & Policese > Device Profiles. Click on a Windows Device profile to Edit it. Or click on the Create New Profile button if you are creating a Windows Profile for the first time.
Once in the Device Profile wizard, navigate to Settings > Security Settings. Go to BitLocker section to configure BitLocker settings.
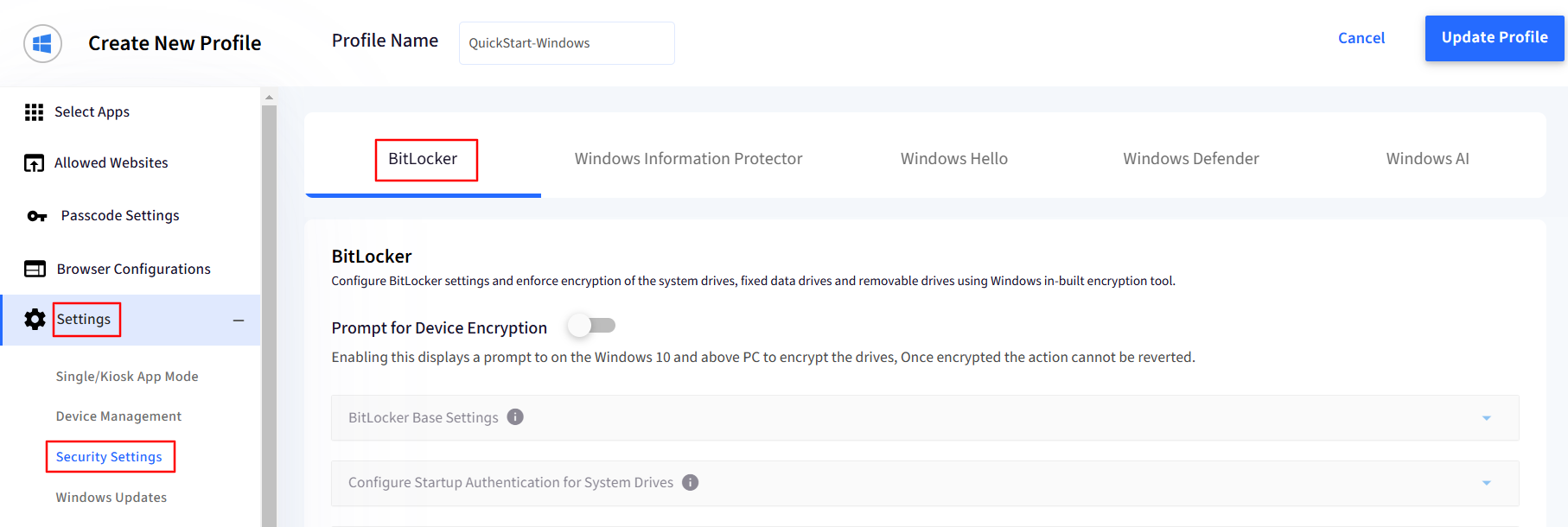
Toggle on the Prompt for Device Encryption button. This will make the BitLocker settings under it accessible.
BitLocker Settings
The following are the BitLocker settings that you can configure to encrypt the Windows devices.
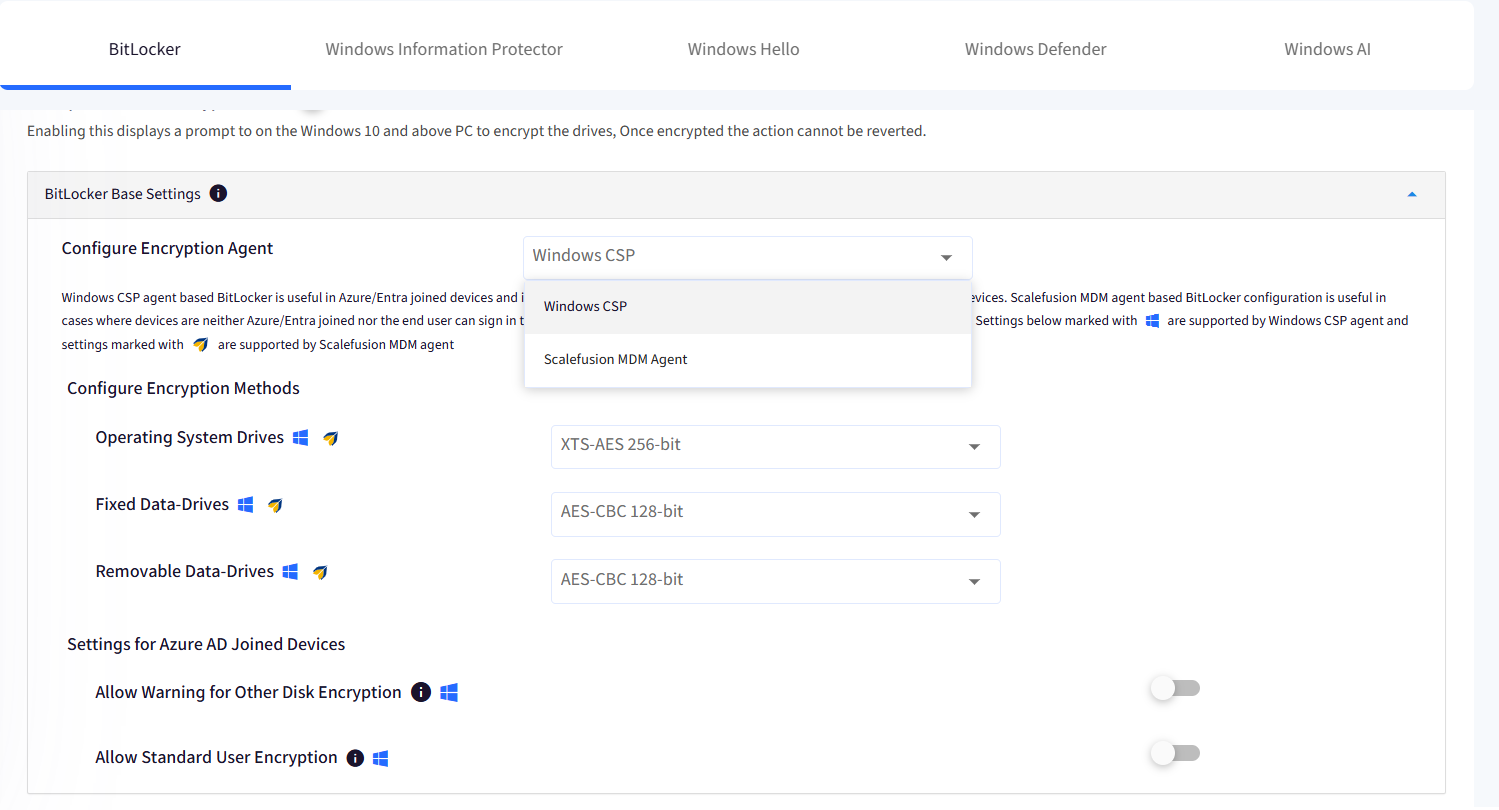
A. BitLocker Base Settings
The first section controls the basic encryption settings.
Configure Encryption Agent: Select how the BitLocker encryption will apply to the device. Select Windows CSP from the drop-down menu list.
Windows CSP agent-based BitLocker is useful in Azure/Entra joined devices and in cases where end users can sign in to their Microsoft Accounts like in BYOD devices.
Note:
Settings marked with
 are supported by Windows CSP agent and settings marked with
are supported by Windows CSP agent and settings marked with  are supported by Scalefusion MDM agent
are supported by Scalefusion MDM agent
Configure Encryption Methods: Choose an encryption algorithm for the various disk drives.
Operating System Drives: Defaults to XTS-AES 256-bit
Fixed Data Drives: Defaults to AES-CBC 128-bit
Removable Data Drives: Defaults to AES-CBC 128-bit
Settings for Azure AD joined Devices: These settings apply only to devices enrolled using the AD join method.
Allow Warning for Other Disk Encryption: Enable this to show a warning for AD-joined devices. Disabling this silently applies the BitLocker settings.
Allow Standard User Encryption: Enable this to encrypt all the disk drives for a standard user account.
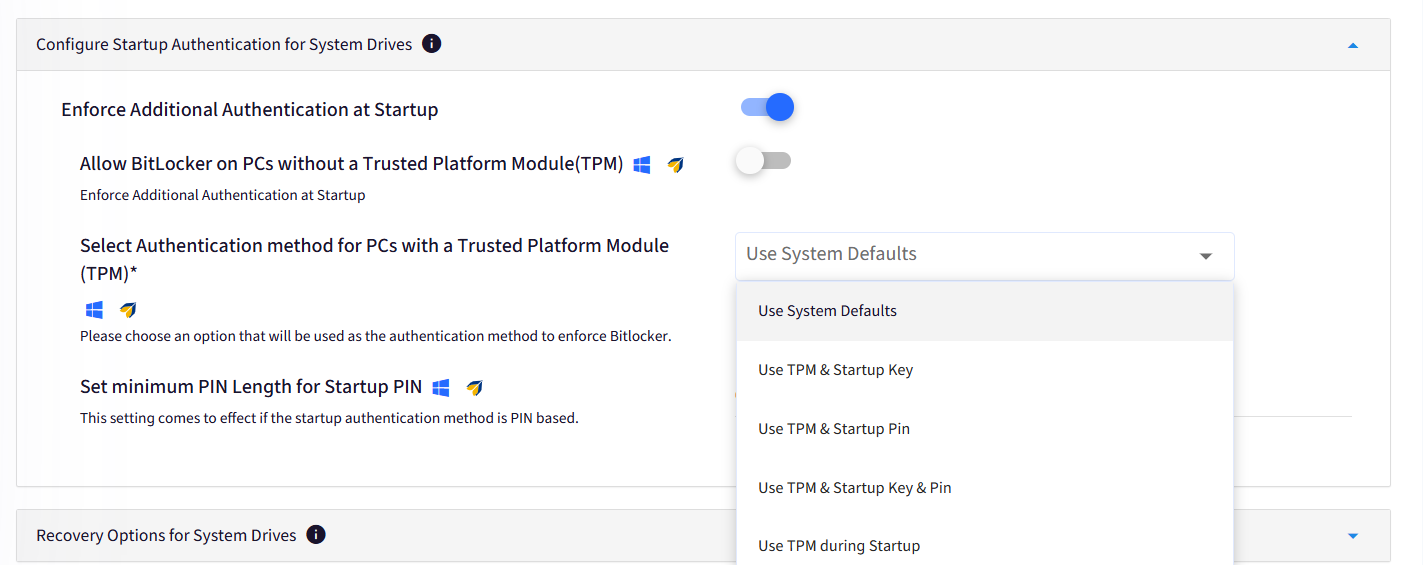
B. Configure Startup Authentication for System Drives
Use this section to configure additional authentication methods when the computer starts and configure settings for computers with/without a TPM chip.
Enforce Additional Authentication at Startup: Enable this setting to configure additional authentication mechanisms.
Allow BitLocker on PCs without a Trusted Platform Module(TPM): Configure BitLocker for computers without a TPM chip.
The user must insert a USB startup key to start the computer or resume from hibernation.
Select Authentication method for PCs with a Trusted Platform Module: Select the authentication method. Users will see only the selected options while configuring BitLocker.
Set Minimum Length for Startup PIN: Enforce a minimum PIN length that needs to be configured.
This setting works only if the authentication method includes a PIN.
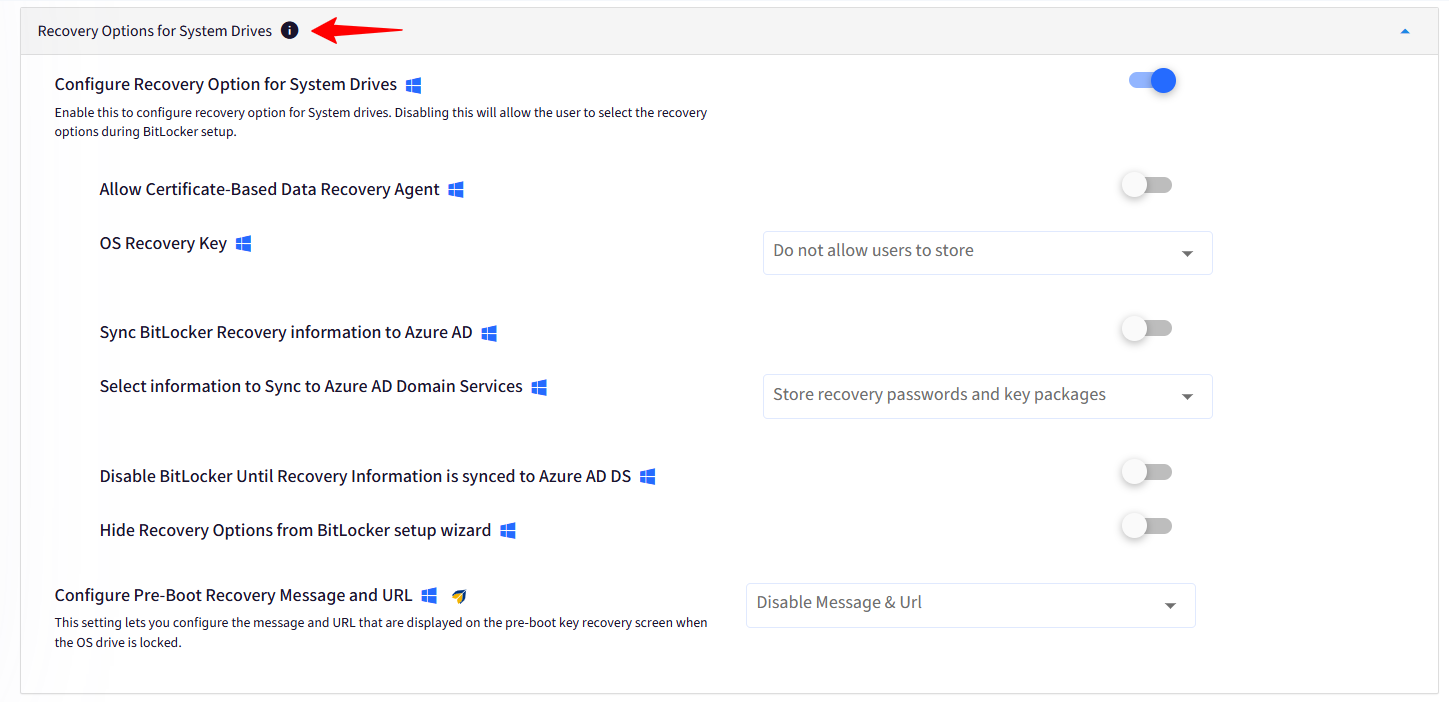
C. Recovery Options for System Drives
If you have configured the startup authentication, then this method allows you to configure the recovery mechanisms for System drives (the drive that hosts the OS).
Configure Recovery Option for System Drives: Enable this to configure the recovery options.
Allow Certificate-Based Data Recovery Agent: Specify whether a data recovery agent can be used with BitLocker-protected operating system drives. Before a data recovery agent can be used it must be added from the Public Key Policies item in either the Group Policy Management Console or the Local Group Policy Editor.
OS Recovery Key: Configure if users are allowed, required, or not allowed to generate a 48-digit recovery password or a 256-bit recovery key.
Sync BitLocker Recovery Information to Azure AD: Enable this to Sync the BitLocker recovery/escrow keys to Azure AD. This setting works only if the device is Azure AD joined.
Select information to Sync to Azure AD Domain Services: Choose what information related to BitLocker recovery should be used to sync with Azure AD.
Disable BitLocker Until Recovery Information is synced to Azure AD DS: Prevent users from configuring BitLocker until they join their devices to Azure AD.
Hide Recovery Options from BitLocker setup wizard: Prevent users from specifying recovery options when they turn on BitLocker on a drive. This means that you will not be able to specify which recovery option to use when you turn on BitLocker, instead, BitLocker recovery options for the drive are determined by the policy setting.
Configure Pre-boot Recovery Message and URL: Override the default pre-boot recovery message and URL that is displayed when the computer starts.
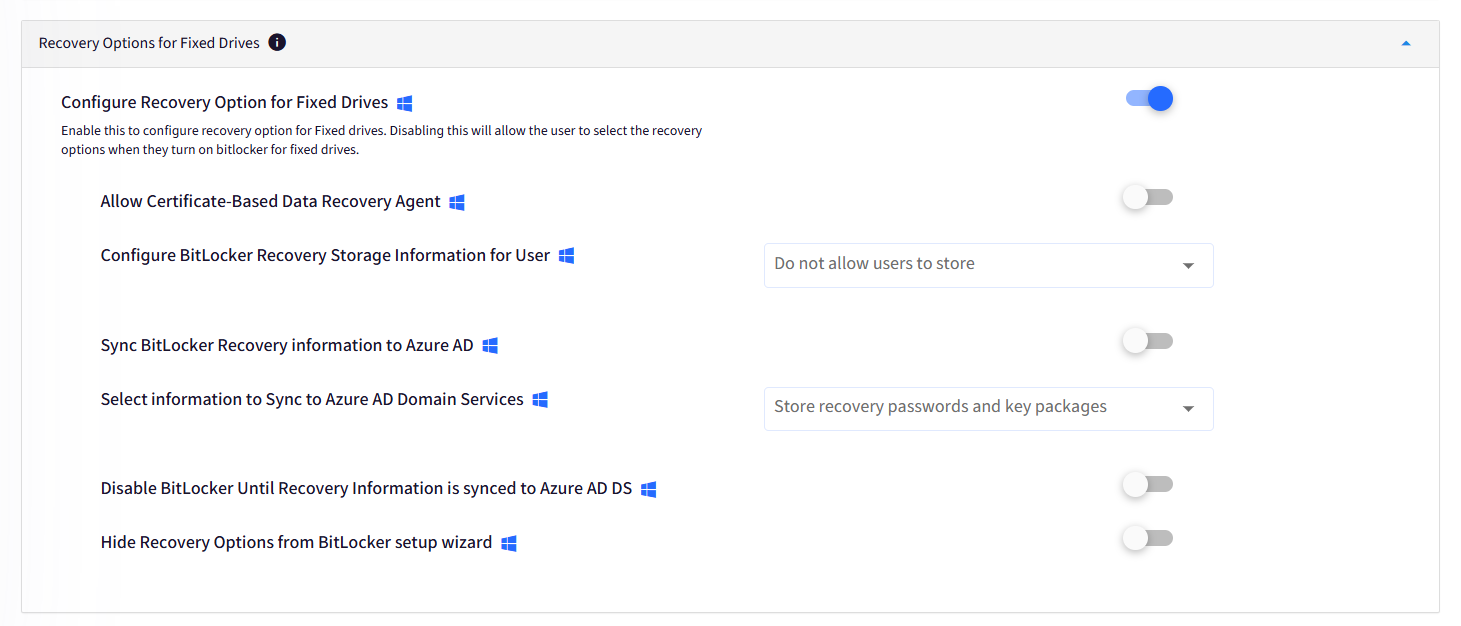
D. Recovery Option for Fixed Drives
Configure recovery options for your fixed drives. These options are similar to the Recovery Options for System Drives, as seen previously in Point C; except that these are set for the non-System or other fixed drive partitions.
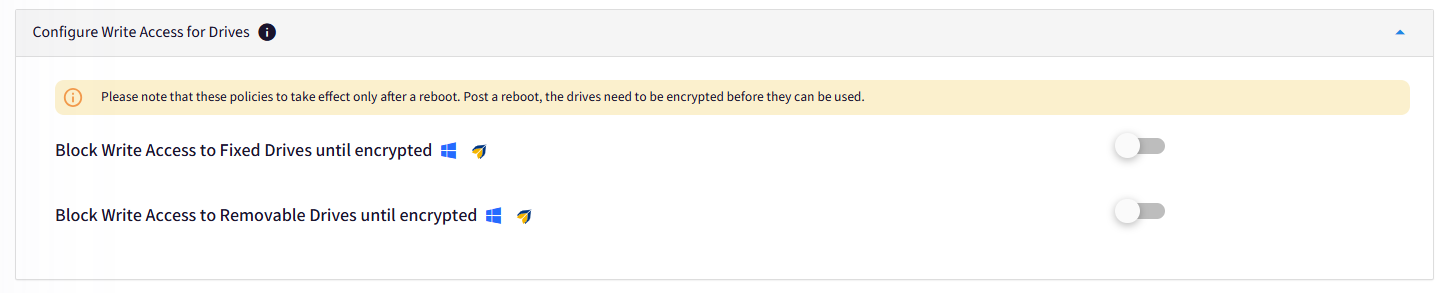
E. Configure Write Access for Drives
Configure if users are allowed to write data or create files on the fixed drives and removable media without BitLocker encryption.
Block Write Access to Fixed Device until encrypted: If enabled blocks write access to fixed drives until they are encrypted.
Block Write Access to Removable Devices until encrypted: If enabled blocks write access to removable drives.
Note:
The existing data stored on these drives can be read always.
F. Configure Scalefusion MDM Agent based Settings
The settings in this section will only apply if the Scalefusion MDM agent is chosen in the "Configure Encryption Agent" section of the BitLocker Base Settings. Please refer to our guide on how these settings work.
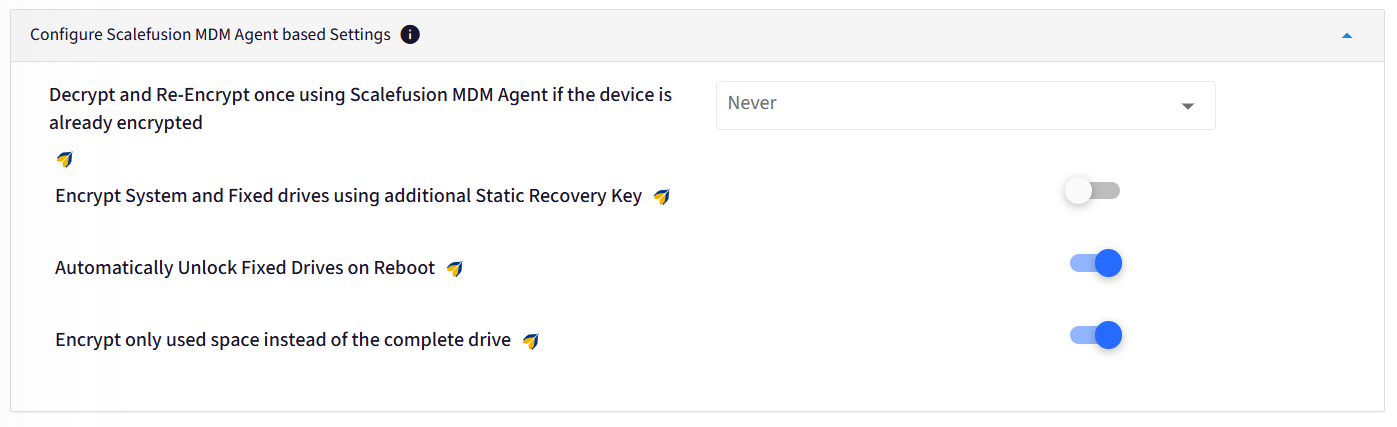
Once you have configured your BitLocker settings, click on Update Profile to save these settings. The changes will be automatically pushed to the devices where this profile is applied.
User Experience for BitLocker Setup on Device
Now that you have configured a BitLocker policy, let us have a look at the user experience while they configure BitLocker. The actual flow may be different and is dependent on your BitLocker policy.
For Azure AD joined devices, BitLocker encryption will happen automatically if Allow Warning for Disk Encryption is disabled.
Once a BitLocker policy is configured, the end users will see a notification in the system tray, prompting them to configure BitLocker.
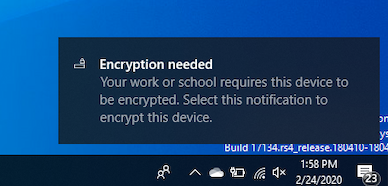
Clicking on the notification starts the encryption process. Select Yes to start encryption.
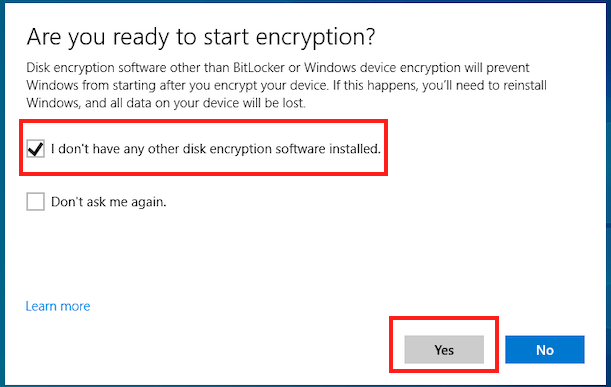
Windows verifies if BitLocker can be configured and if supported then it shows the Start up authentication configuration screen basing on the policy. Here the user has an option to create a PIN or a recovery key using USB drive.
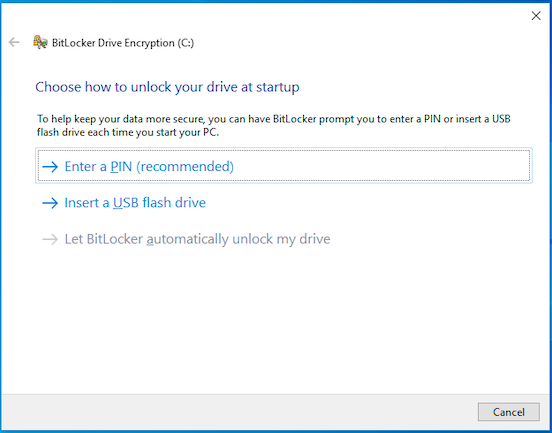
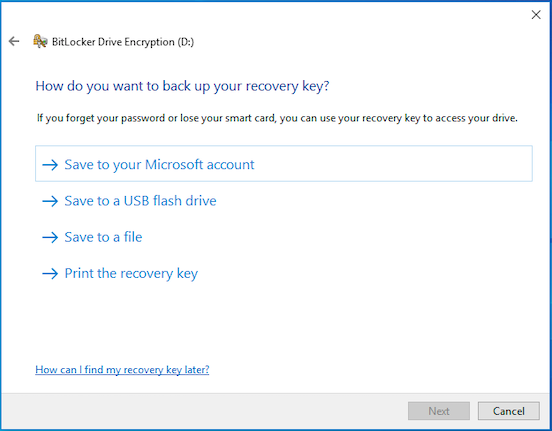
Next, they are shown the recovery options for System drive basing on the policy. Here they can select how to back up the recovery key. Select an option to back up and click Next.
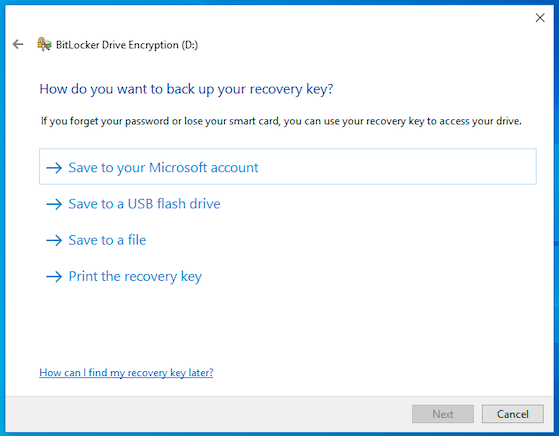
Next, they get an option to back up the recovery key for fixed drives if configured in the policy. Select an option to back up and click Next.
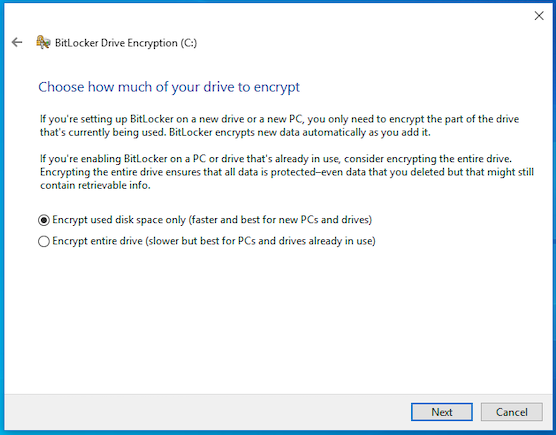
Next, select how to encrypt the drives where they can choose to Encrypt used space or Encrypt the complete drive. Click Next.
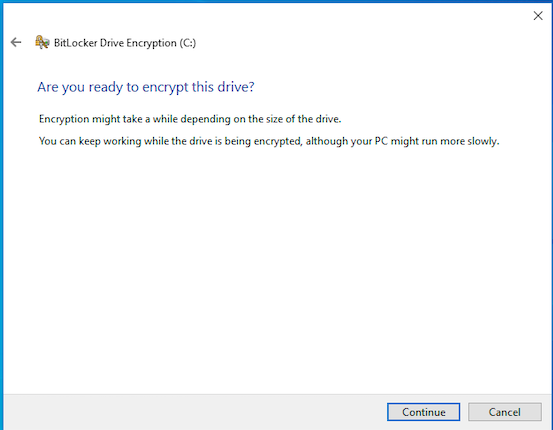
The final step is to confirm the process and start the encryption. Click Continue to start the encryption.
Possible Conflicting Scenarios
Due to the wide variety of options available for BitLocker and some of them being interdependent, there is a chance that some of these settings may cause conflict and may not work on actual device even though the policy gets successfully applied. In case of a conflict when users try to configure BitLocker on their device, they see an error. Here we cover some of the settings that may cause possible conflicts.
Devices without a TPM Chip: For devices without a TPM chip, BitLocker cannot encrypt System/OS drives until "Allow BitLocker on PCs without Trusted Platform Module (TPM)" is enabled.

Startup Authentication Methods: Startup authentication mechanisms are mutually exclusive at this point of time, that is both PIN & Recovery key cannot be used. Although we have given this option for future support. The setting below is an invalid option.
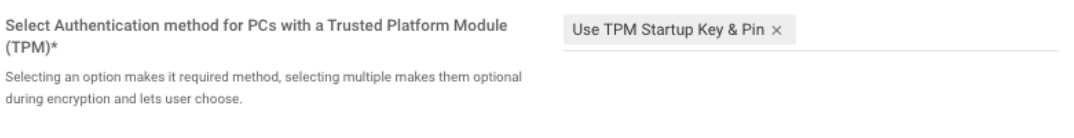
Error on Device
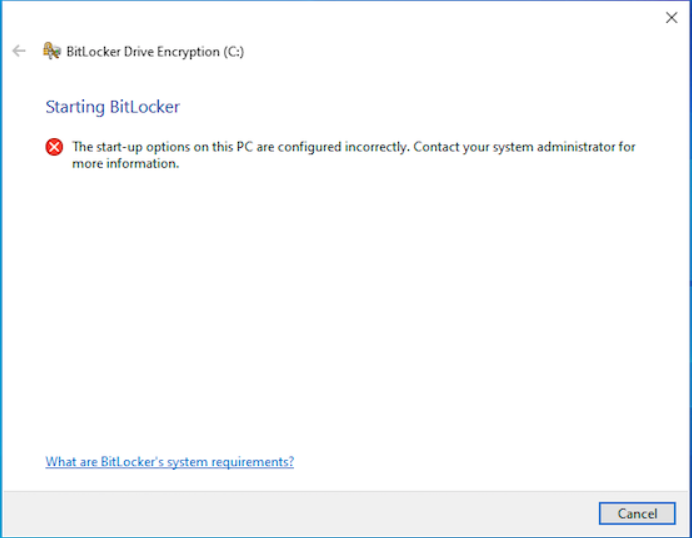
Recovery Options for System Drive: If the recovery options are not configured properly then you may see the following error on Device.
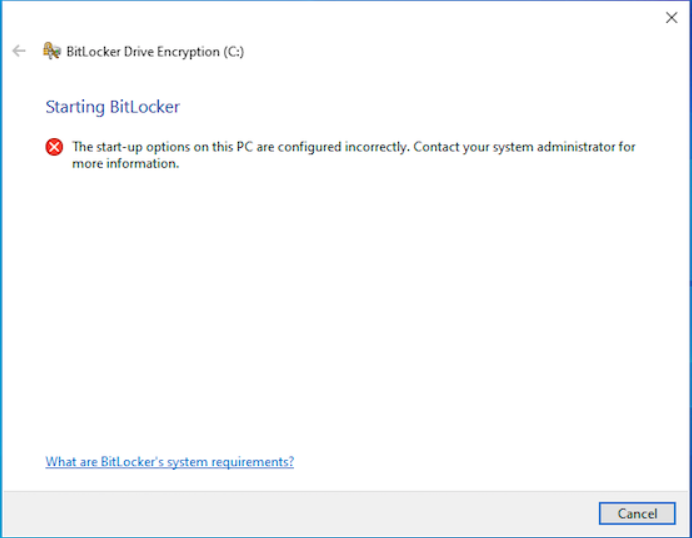
Conflict 1: If Startup Authentication mechanism is Use TPM Startup PIN then the OS Recovery Key cannot be set to Do not allow users to store. The setting below is an invalid combination.
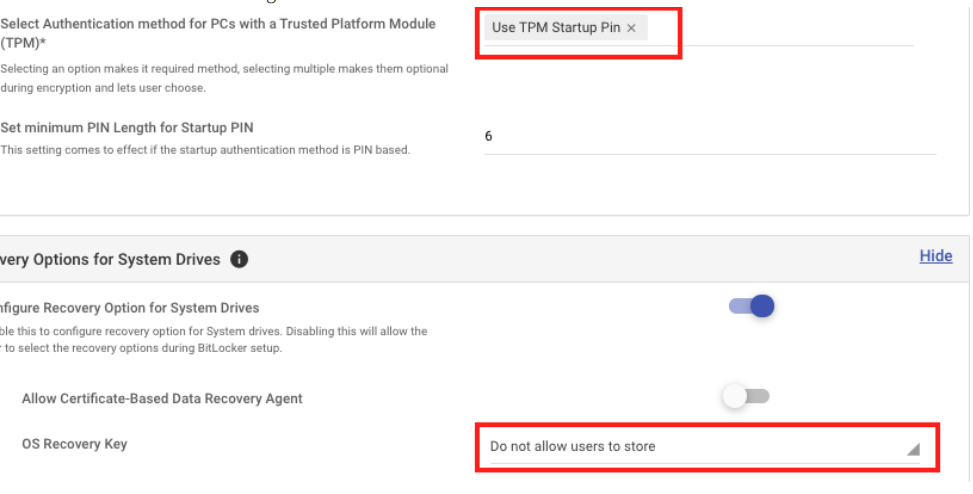
Conflict 2: If Startup Authentication mechanism is Use TPM Startup Key then OS Recovery Key cannot be set to Allow users to generate the recovery password OR Enforce users to generate Recovery Password
If the Write access to Fixed Drives is Blocked then the the OS Recovery Key cannot be set to Allow users to generate Recovery Key or Enforce users to generate Recovery Key.
Note:
For the above settings to work on Windows 11 devices, a Microsoft account should be present on the target device(s). In case there is no Microsoft account available, you can silently enable Bitlocker encryption using the PowerShell script (please refer our guide on the same).